A uniform stationary ladder of length l stands as a ubiquitous tool in various industrial and domestic settings. Its physical attributes, static equilibrium, stability, and diverse applications make it an indispensable subject of study for engineers, architects, and safety professionals.
This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricacies of uniform stationary ladders, providing a foundation for understanding their design, usage, and limitations.
The subsequent paragraphs will delve into the ladder’s physical dimensions, static equilibrium, stability considerations, and practical applications. By examining these aspects, we aim to provide a holistic understanding of uniform stationary ladders, enabling readers to optimize their use and ensure safety.
Ladder’s Physical Attributes
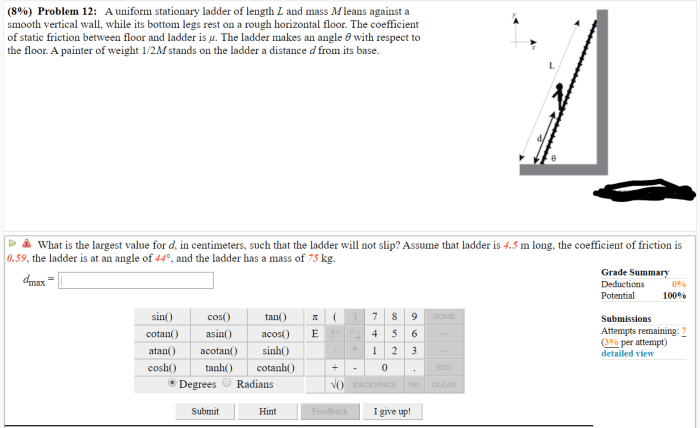
A uniform stationary ladder is characterized by its specific dimensions and material composition, which influence its properties and suitability for various applications.
Ladder’s Dimensions and Measurements, A uniform stationary ladder of length l
The ladder’s length (l) is a crucial measurement that determines the maximum height it can reach when placed against a surface. The length of the ladder is typically measured in feet or meters and can vary depending on the intended use.
Significance of Ladder’s Length
The ladder’s length determines the range of tasks it can be used for. Longer ladders are suitable for reaching higher elevations, while shorter ladders are more appropriate for smaller tasks or indoor use.
Material Composition and Impact on Properties
Ladders can be made from various materials, including aluminum, fiberglass, or wood. The material composition affects the ladder’s weight, durability, and safety characteristics. Aluminum ladders are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, while fiberglass ladders are non-conductive and suitable for electrical work. Wood ladders are more traditional but can be heavier and require regular maintenance.
Ladder’s Static Equilibrium
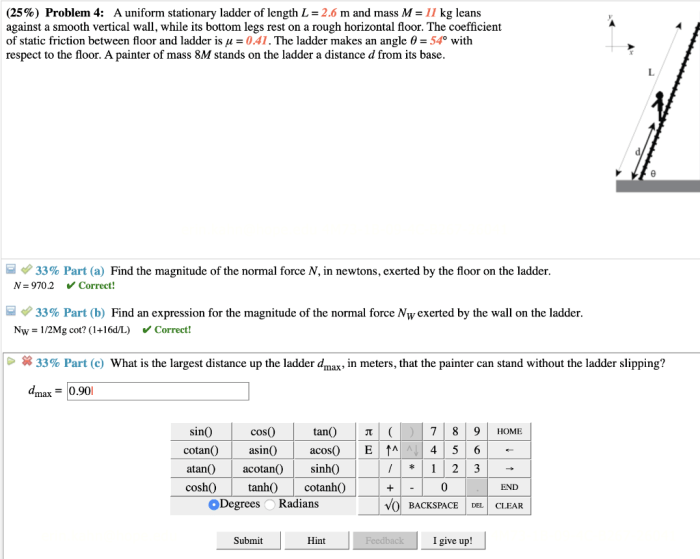
A uniform stationary ladder is in uniform stationary equilibrium when it is positioned against a surface and does not experience any net force or torque. This equilibrium is essential for safe and stable use of the ladder.
Diagram of Forces Acting on the Ladder
When the ladder is in equilibrium, the forces acting on it include the weight of the ladder (W), the normal force exerted by the surface (N), and the friction force (F) between the ladder and the surface.
Conditions for Equilibrium
For the ladder to remain in equilibrium, the following conditions must be met:
- The sum of the forces in the vertical direction must be zero (W = N).
- The sum of the forces in the horizontal direction must be zero (F = 0).
- The sum of the torques about any point must be zero (the ladder is not rotating).
Ladder’s Stability and Safety
The stability of a uniform stationary ladder is crucial for safe use. Several factors influence the ladder’s stability, including the angle of inclination and the surface conditions.
Factors Affecting Ladder’s Stability
The angle of inclination is a significant factor affecting the ladder’s stability. The steeper the angle, the less stable the ladder becomes. Additionally, uneven or slippery surfaces can compromise the ladder’s stability.
Importance of Angle of Inclination
For safe usage, the angle of inclination should be approximately 75 degrees from the vertical. This angle provides a balance between stability and reach.
Safety Precautions and Best Practices
To ensure safe ladder usage, it is essential to follow best practices, including:
- Inspecting the ladder before use for any damage or defects.
- Setting up the ladder on a stable and level surface.
- Ensuring the ladder extends at least three feet above the landing surface.
- Maintaining three points of contact with the ladder (two hands and a foot or two feet and a hand) while climbing or descending.
- Avoiding overreaching or leaning too far to the side.
Ladder’s Applications
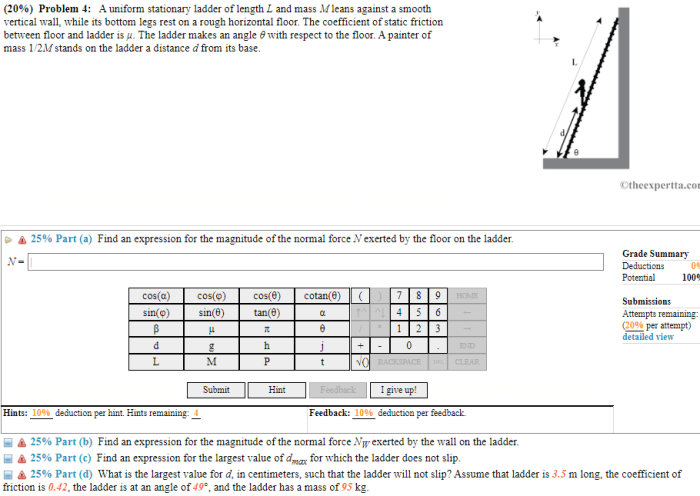
Uniform stationary ladders are widely used in various applications, including:
Common Applications
- Accessing rooftops for maintenance or repairs.
- Reaching high shelves in warehouses or libraries.
- Performing electrical work or other tasks requiring elevation.
- Cleaning windows or other tall surfaces.
- Painting or decorating at heights.
Influence of Ladder’s Length and Stationary Nature
The ladder’s length determines the maximum height it can reach, making it suitable for specific tasks. The stationary nature of the ladder provides stability and allows for safe and efficient work at heights.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages of using a uniform stationary ladder include its simplicity, affordability, and ease of use. However, its limited reach and lack of mobility can be limiting in certain situations.
Commonly Asked Questions: A Uniform Stationary Ladder Of Length L
What is the significance of the ladder’s length (l)?
The length of the ladder (l) is a crucial factor that determines its reach and stability. A longer ladder allows access to higher elevations but requires additional support to maintain equilibrium.
How does the angle of inclination affect the ladder’s stability?
The angle of inclination is a critical factor in maintaining the ladder’s stability. A steeper angle reduces the ladder’s base of support, making it more prone to tipping. The recommended angle of inclination for safe usage is generally between 75 and 78 degrees.
What are some common applications of uniform stationary ladders?
Uniform stationary ladders are commonly used in construction, painting, maintenance, and other tasks that require reaching elevated areas. They are particularly suitable for situations where frequent repositioning is not necessary.