Enduring issues essay outline global history – With enduring issues essay Artikel global history at the forefront, this exploration delves into the profound struggles, disparities, and transformations that have shaped human civilization. From political power dynamics to economic inequalities, environmental degradation to cultural diversity, and the intricate interplay of war and peace, this Artikel provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the enduring challenges that have defined our past and continue to resonate in the present.
Throughout history, humanity has grappled with the quest for political power and social equality, leading to pivotal events and movements that have left an indelible mark on the global landscape. Economic disparities, rooted in colonialism and globalization, have fueled social unrest and political instability, while environmental degradation and climate change pose unprecedented threats to human societies and the planet’s well-being.
1. Enduring Political and Social Struggles
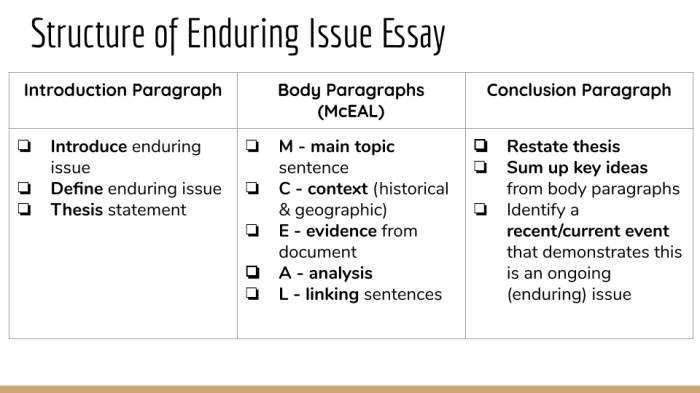
Throughout history, humans have engaged in persistent struggles for political power and social equality. These struggles have shaped the course of civilizations, leading to revolutions, wars, and social movements.
Key Events and Movements
- French Revolution (1789): A pivotal moment in the fight for democracy and human rights.
- American Civil War (1861-1865): A conflict over slavery that transformed the United States.
- Civil Rights Movement (1950s-1960s): A nonviolent campaign that fought for racial equality in the United States.
- Tiananmen Square protests (1989): A student-led movement that challenged authoritarian rule in China.
- Arab Spring (2010s): A series of popular uprisings that aimed to overthrow dictatorships in the Middle East.
Ideologies and Perspectives
- Liberalism: Advocates for individual freedom, limited government, and economic opportunity.
- Socialism: Calls for the redistribution of wealth and the establishment of a more egalitarian society.
- Nationalism: Emphasizes loyalty to one’s nation and culture.
- Marxism: Argues that capitalism leads to class struggle and the exploitation of workers.
- Feminism: Advocates for gender equality and women’s rights.
2. Economic Inequality and Global Trade
Economic inequality has been a persistent issue throughout history, with significant consequences for global development. The emergence of capitalism and globalization has exacerbated these disparities.
Historical Roots of Inequality
- Feudalism: A medieval system that concentrated wealth and power in the hands of a few.
- Mercantilism: An economic policy that promoted national wealth through trade and colonization.
- Industrial Revolution: Led to a widening gap between the wealthy elite and the working class.
Role of Colonialism and Imperialism
- European colonization exploited resources and labor in Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- Imperialism created economic dependencies that perpetuated inequality between nations.
Impact of Globalization
- Increased trade and investment have led to economic growth but also job losses and wage stagnation in some regions.
- Multinational corporations often exploit cheap labor in developing countries.
- Economic inequality can lead to social unrest and political instability.
3. Environmental Degradation and Climate Change

Human activities have had a profound impact on the environment, leading to degradation and climate change. These issues pose significant challenges for the future of humanity.
Historical Origins of Environmental Degradation
- Deforestation: Large-scale clearing of forests for agriculture and other purposes.
- Pollution: Industrialization and urbanization have released harmful substances into the air, water, and soil.
- Overpopulation: The rapid growth of the human population has increased pressure on resources.
Impact of Industrialization and Consumption
- Burning of fossil fuels has released greenhouse gases, leading to climate change.
- Mass production and consumption have created large amounts of waste and pollution.
Global Challenges and Opportunities
- Climate change: Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and other consequences threaten human societies.
- Renewable energy: Transitioning to sustainable energy sources is essential to mitigate climate change.
- Conservation: Protecting ecosystems and biodiversity is crucial for maintaining a healthy planet.
4. Cultural Diversity and Intercultural Exchange: Enduring Issues Essay Outline Global History
Cultural diversity is a defining feature of human history. Interactions between different cultures have led to both conflict and cooperation.
Development of Cultural Diversity, Enduring issues essay outline global history
- Human migrations and settlements have created a wide range of cultural traditions.
- Geographical barriers and social divisions have contributed to cultural diversity.
Processes of Cultural Exchange
- Trade: Goods, ideas, and technologies have been exchanged through trade routes.
- Migration: People have moved across borders, bringing their cultures with them.
- Technology: Communication and transportation advances have facilitated cultural interactions.
Impact of Cultural Interactions
- Assimilation: Cultures may blend and adapt to form new traditions.
- Conflict: Cultural differences can lead to misunderstandings and tensions.
- Enrichment: Cultural exchange can promote innovation and creativity.
5. War and Peace

War and conflict have been a persistent feature of human history, but there have also been periods of peace and cooperation.
Causes of War
- Political disputes: Competition for power and resources.
- Ideological differences: Clashes between opposing beliefs.
- Economic inequality: Disparities can lead to resentment and conflict.
Evolution of Warfare
- Technological advancements: Weapons and strategies have become more sophisticated.
- Total war: Modern warfare has involved the mobilization of entire societies.
- Nuclear weapons: The development of nuclear weapons has raised the stakes of conflict.
Challenges and Opportunities for Peace
- Diplomacy: Negotiation and mediation can resolve conflicts peacefully.
- International organizations: The United Nations and other organizations promote cooperation and peace.
- Peacebuilding: Post-conflict efforts aim to rebuild societies and prevent future violence.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of studying enduring issues in global history?
Examining enduring issues in global history allows us to identify patterns, learn from past mistakes, and develop strategies for addressing contemporary challenges.
How does economic inequality impact global stability?
Economic inequality can lead to social unrest, political instability, and conflict, as marginalized populations seek to address their grievances.
What are the root causes of environmental degradation?
Environmental degradation is primarily driven by industrialization, population growth, and unsustainable resource consumption.
How does cultural diversity contribute to global understanding?
Cultural diversity fosters mutual respect, empathy, and a broader perspective on human experiences and values.
What are the key factors that influence the outbreak of war?
War can be triggered by political, economic, social, and ideological factors, often intertwined in complex ways.