The price p in dollars and the quantity x sold – The equilibrium of price P in dollars and quantity X sold is a fundamental concept in economics that elucidates the dynamic interplay between supply and demand. This concept underpins the allocation of resources, the formation of prices, and the efficient functioning of markets.
This exploration will delve into the intricate relationship between price and quantity, examining the factors that influence their equilibrium and the implications for market dynamics. We will unravel the intricacies of demand and supply functions, equilibrium price and quantity, shifts in demand and supply, elasticity, market efficiency, government intervention, and real-world applications.
Demand Function: The Price P In Dollars And The Quantity X Sold
A demand function is a mathematical equation that represents the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded by consumers. It shows how changes in price affect the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy.
The demand function is typically written as:
Qd= f(P)
Where:
- Q dis the quantity demanded
- P is the price
- f(P) is a function that represents the relationship between price and quantity demanded
For example, the demand function for a particular good might be:
Qd= 100
2P
This equation shows that as the price of the good increases, the quantity demanded decreases. Specifically, for every $1 increase in price, the quantity demanded decreases by 2 units.
Supply Function
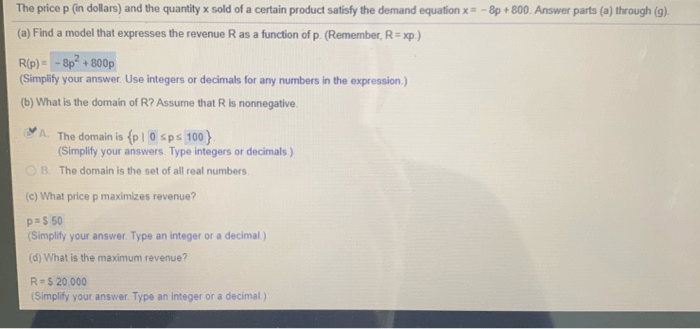
A supply function is a mathematical equation that represents the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied by producers. It shows how changes in price affect the amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to sell.
The supply function is typically written as:
Qs= f(P)
Where:
- Q sis the quantity supplied
- P is the price
- f(P) is a function that represents the relationship between price and quantity supplied
For example, the supply function for a particular good might be:
Qs= 50 + 3P
This equation shows that as the price of the good increases, the quantity supplied increases. Specifically, for every $1 increase in price, the quantity supplied increases by 3 units.
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
The equilibrium price and quantity are the values of price and quantity at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. At this point, there is no shortage or surplus of the good or service in the market.
To find the equilibrium price and quantity, we set the demand function equal to the supply function and solve for P and Q.
For example, if the demand function is Q d= 100 – 2P and the supply function is Q s= 50 + 3P, we can solve for the equilibrium price and quantity as follows:
- 100
- 2P = 50 + 3P
- = 5P
P = 10
Qd= 100
2(10) = 80
Q s= 50 + 3(10) = 80
Therefore, the equilibrium price is $10 and the equilibrium quantity is 80 units.
Shifts in Demand and Supply
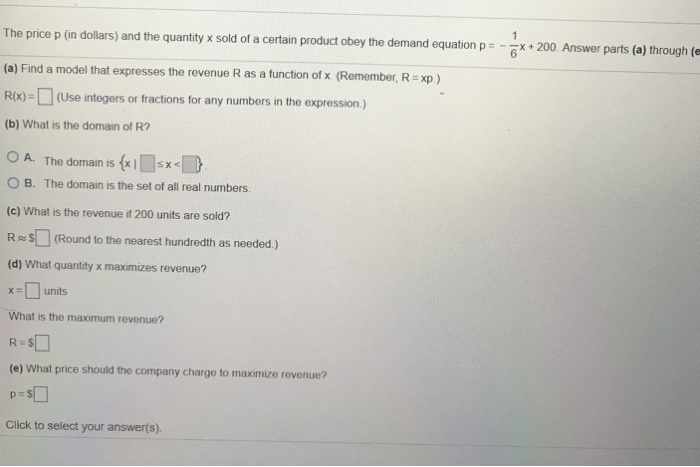
The demand and supply functions can shift in response to changes in factors such as consumer preferences, technology, and government policies.
Shifts in Demand
Factors that can cause shifts in demand include:
- Changes in consumer tastes and preferences
- Changes in consumer income
- Changes in the prices of related goods
- Changes in expectations about future prices
Shifts in Supply, The price p in dollars and the quantity x sold
Factors that can cause shifts in supply include:
- Changes in the cost of production
- Changes in technology
- Changes in government regulations
- Changes in the number of producers
Shifts in demand and supply can have a significant impact on equilibrium price and quantity. For example, an increase in demand will lead to an increase in equilibrium price and quantity, while a decrease in supply will lead to an increase in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity.
Elasticity
Elasticity is a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded or supplied to changes in price.
There are different types of elasticity, including:
- Price elasticity of demand
- Price elasticity of supply
- Income elasticity of demand
- Cross-price elasticity of demand
Elasticity can be used to predict how consumers and producers will respond to changes in price. For example, a good with a high price elasticity of demand is likely to experience a large decrease in quantity demanded when the price increases.
Market Efficiency

Market efficiency refers to the ability of a market to allocate resources efficiently. An efficient market is one in which the equilibrium price and quantity are the optimal values for society.
The conditions necessary for market efficiency include:
- Perfect competition
- No externalities
- Perfect information
When these conditions are met, the market will allocate resources efficiently and there will be no need for government intervention.
Government Intervention
Government intervention in the market can take many forms, including:
- Price controls
- Quantity controls
- Subsidies
- Taxes
Government intervention can have a significant impact on equilibrium price and quantity. For example, a price ceiling will lower the equilibrium price and increase the quantity demanded, while a price floor will raise the equilibrium price and decrease the quantity demanded.
Applications in Real-World Markets
The concepts of supply and demand are used in a variety of real-world markets. For example, businesses use supply and demand to set prices, predict consumer behavior, and make production decisions.
Understanding supply and demand is essential for making informed economic decisions. By understanding how these concepts work, businesses and consumers can make better decisions about what to buy, sell, and produce.
Common Queries
What is the demand function?
The demand function is a mathematical equation that expresses the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded by consumers.
What is the supply function?
The supply function is a mathematical equation that expresses the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied by producers.
How is equilibrium price and quantity determined?
Equilibrium price and quantity are determined at the point where the demand and supply functions intersect.