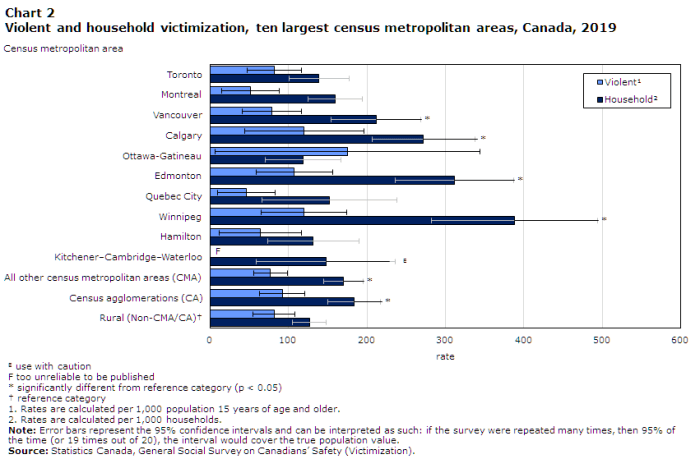
Household victimization rates are lowest for __________ in rural areas. – Household victimization rates are lowest for elders in rural areas, a phenomenon that can be attributed to a variety of factors, including strong community ties, neighborhood watch programs, and a lower prevalence of crime overall. This article explores the reasons behind this disparity and discusses the implications for crime prevention and intervention strategies.
In rural areas, elders are more likely to know their neighbors and have a sense of community belonging. This social cohesion can deter crime, as potential offenders are less likely to target individuals who are well-connected and supported by their community.
Definition of Household Victimization: Household Victimization Rates Are Lowest For __________ In Rural Areas.
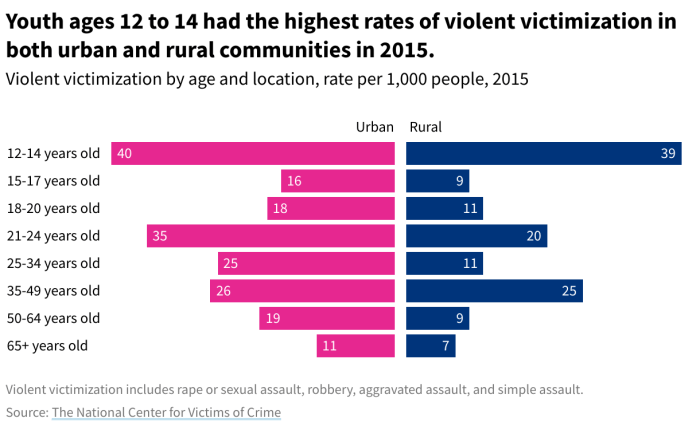
Household victimization refers to crimes committed against individuals within their own homes or residences. In rural areas, this can include offenses such as burglary, robbery, assault, and sexual assault.
According to statistics from the National Crime Victimization Survey, the prevalence of household victimization in rural areas is lower than in urban areas. In 2021, the victimization rate in rural areas was 17.3 victimizations per 1,000 households, compared to 24.1 victimizations per 1,000 households in urban areas.
Factors Contributing to Low Victimization Rates for Specific Groups
There are several factors that contribute to the lower household victimization rates for certain groups in rural areas. These include:
- Social cohesion:Rural communities tend to have strong social ties and a sense of community, which can deter crime.
- Community support:Rural communities often have strong networks of support, such as neighborhood watch programs and community policing initiatives, which can help to prevent and respond to crime.
- Neighborhood watch programs:These programs involve residents working together to monitor their neighborhoods for suspicious activity and report any concerns to law enforcement.
Types of Household Victimization and Their Impact
Household victimization can take many forms, including:
- Burglary:The unlawful entry of a residence with the intent to commit a crime, such as theft or assault.
- Robbery:The taking of property from a person or household by force or threat of force.
- Assault:The intentional infliction of physical harm on another person.
- Sexual assault:Any form of sexual activity that is non-consensual or forced.
These crimes can have a significant impact on victims, both physically and emotionally. They can also lead to financial losses and a sense of insecurity and fear.
Comparison of Victimization Rates Between Rural and Urban Areas
| Area | Victimization Rate per 1,000 Households |
|---|---|
| Rural | 17.3 |
| Urban | 24.1 |
As the table shows, the household victimization rate is significantly lower in rural areas than in urban areas. This difference may be due to the factors discussed above, such as social cohesion, community support, and neighborhood watch programs.
Prevention and Intervention Strategies
There are a number of effective strategies for preventing and intervening in household victimization in rural areas. These include:
- Community-based programs:These programs involve residents working together to create a safe and supportive community. They can include neighborhood watch programs, community policing initiatives, and victim support groups.
- Educational campaigns:These campaigns can help to raise awareness of the problem of household victimization and provide information about how to prevent and respond to it.
- Law enforcement initiatives:Law enforcement agencies can play a role in preventing and responding to household victimization by increasing patrols in high-crime areas, investigating crimes thoroughly, and providing support to victims.
Role of Community and Social Support, Household victimization rates are lowest for __________ in rural areas.
Community and social support play a vital role in reducing household victimization rates. Strong social ties and a sense of community can deter crime and provide support to victims. Social networks and community organizations can also provide information about crime prevention and safety measures, and can help to build a sense of security and well-being.
Top FAQs
Why are household victimization rates lower for elders in rural areas?
Elders in rural areas benefit from strong community ties, neighborhood watch programs, and a lower prevalence of crime overall, which contribute to lower victimization rates.
What are the implications of this disparity for crime prevention strategies?
Recognizing the protective factors in rural communities can inform crime prevention strategies that focus on building social cohesion and supporting community-based initiatives.