Six big ideas in the constitution handout 3 – At the heart of American democracy lies the Constitution, a foundational document that enshrines six big ideas. These ideas, including popular sovereignty, limited government, separation of powers, checks and balances, judicial review, and individual rights, serve as the bedrock upon which the United States has thrived for over two centuries.
From the inception of the nation, these principles have guided the structure and functioning of the government, ensuring a delicate balance between individual liberty and collective governance. In this exploration, we delve into each of these big ideas, examining their significance, historical evolution, and enduring impact on American society.
Popular Sovereignty

Popular sovereignty is the idea that the government’s authority comes from the consent of the people it governs. In a democracy, popular sovereignty is exercised through elections, in which citizens vote for representatives who will make decisions on their behalf.
In the United States, popular sovereignty is enshrined in the Constitution. The Constitution states that “all political power… is vested in the People of the United States.” This means that the government can only exercise the powers that the people have given it.
The people can give the government more or less power through the amendment process.
Examples of Popular Sovereignty
- Voting in elections
- Running for office
- Participating in referendums and initiatives
Importance of Popular Sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is essential for a democracy. It ensures that the government is accountable to the people and that the people have a say in how they are governed.
Limited Government
Limited government is the idea that the government should only have the powers that are necessary to protect the rights of its citizens. This means that the government should not be involved in activities that are not essential to the protection of those rights.
The US Constitution limits the power of government in a number of ways. For example, the Constitution:
- Divides power among the three branches of government (the legislative, executive, and judicial branches)
- Limits the powers of each branch of government
- Protects individual rights
Benefits of Limiting Government Power
There are a number of benefits to limiting government power. These benefits include:
- Protecting individual rights
- Preventing tyranny
- Promoting economic growth
Separation of Powers
The principle of separation of powers is the idea that the three branches of government (the legislative, executive, and judicial branches) should be separate and independent from each other. This separation of powers helps to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
The US Constitution divides power among the three branches of government in a number of ways. For example, the Constitution:
- Gives the legislative branch the power to make laws
- Gives the executive branch the power to enforce laws
- Gives the judicial branch the power to interpret laws
Advantages of Separating Powers
There are a number of advantages to separating powers. These advantages include:
- Preventing any one branch of government from becoming too powerful
- Ensuring that the government is accountable to the people
- Protecting individual rights
Disadvantages of Separating Powers
There are also some disadvantages to separating powers. These disadvantages include:
- Can lead to gridlock and inefficiency
- Can make it difficult to respond to crises
Checks and Balances
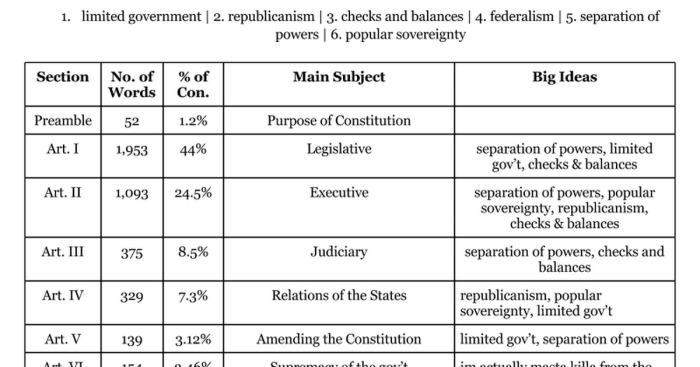
Checks and balances is a system of government in which each branch of government has the power to limit the powers of the other branches. This system helps to ensure that no one branch of government becomes too powerful.
The US Constitution includes a number of checks and balances. For example, the Constitution:
- Gives the president the power to veto laws passed by Congress
- Gives Congress the power to override presidential vetoes
- Gives the Supreme Court the power to declare laws unconstitutional
Importance of Checks and Balances
Checks and balances are essential for a democracy. They help to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful and they help to protect individual rights.
Judicial Review
Judicial review is the power of the courts to declare laws unconstitutional. This power helps to ensure that the government does not violate the rights of its citizens.
The US Constitution does not explicitly grant the courts the power of judicial review. However, the Supreme Court established the principle of judicial review in the case of Marbury v. Madison (1803).
Examples of Judicial Review
The Supreme Court has used the power of judicial review to strike down a number of laws, including:
- Laws that violate the First Amendment
- Laws that violate the Equal Protection Clause
- Laws that violate the Due Process Clause
Pros and Cons of Judicial Review
There are both pros and cons to judicial review. Some of the pros of judicial review include:
- Helps to protect individual rights
- Prevents the government from becoming too powerful
Some of the cons of judicial review include:
- Can lead to gridlock and inefficiency
- Can make it difficult for the government to respond to crises
Individual Rights: Six Big Ideas In The Constitution Handout 3
Individual rights are the rights that all people have simply because they are human beings. These rights include the right to life, liberty, and property.
The US Constitution protects a number of individual rights, including:
- The right to freedom of speech
- The right to freedom of religion
- The right to bear arms
- The right to due process of law
Importance of Protecting Individual Rights, Six big ideas in the constitution handout 3
Individual rights are essential for a free and democratic society. They protect people from the tyranny of the government and they allow people to live their lives as they choose.
FAQ Resource
What is the principle of popular sovereignty?
Popular sovereignty holds that the government derives its authority from the consent of the governed, ensuring that power ultimately resides with the people.
How does the Constitution limit the power of government?
The Constitution establishes a system of limited government by dividing power among different branches, reserving certain powers for the states, and incorporating a Bill of Rights that protects individual freedoms.
What are the advantages of separating powers?
Separation of powers prevents any one branch of government from becoming too powerful, promotes accountability, and ensures a more balanced and deliberative decision-making process.